Salmon is a favorite fish celebrated for its impressive nutritional profile. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality protein, and a range of essential vitamins and minerals, salmon is a powerhouse for supporting overall health and wellbeing. Understanding Salmon Nutrition Facts allows us to make informed choices when planning a balanced diet.
However, some people wonder if salmon has any unhealthy aspects. Exploring its nutritional profile and addressing potential concerns like mercury and PCBs can provide a clearer perspective. This article dives into both the health benefits and potential risks of consuming salmon, offering a comprehensive understanding of its impact on your health.
To fully enjoy the advantages salmon offers, it’s crucial to recognize its Salmon Nutrition Facts, including its high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and vitamins. At the same time, staying mindful of its potential risks ensures we can make smart dietary decisions to maximize the benefits of this nutritious fish.
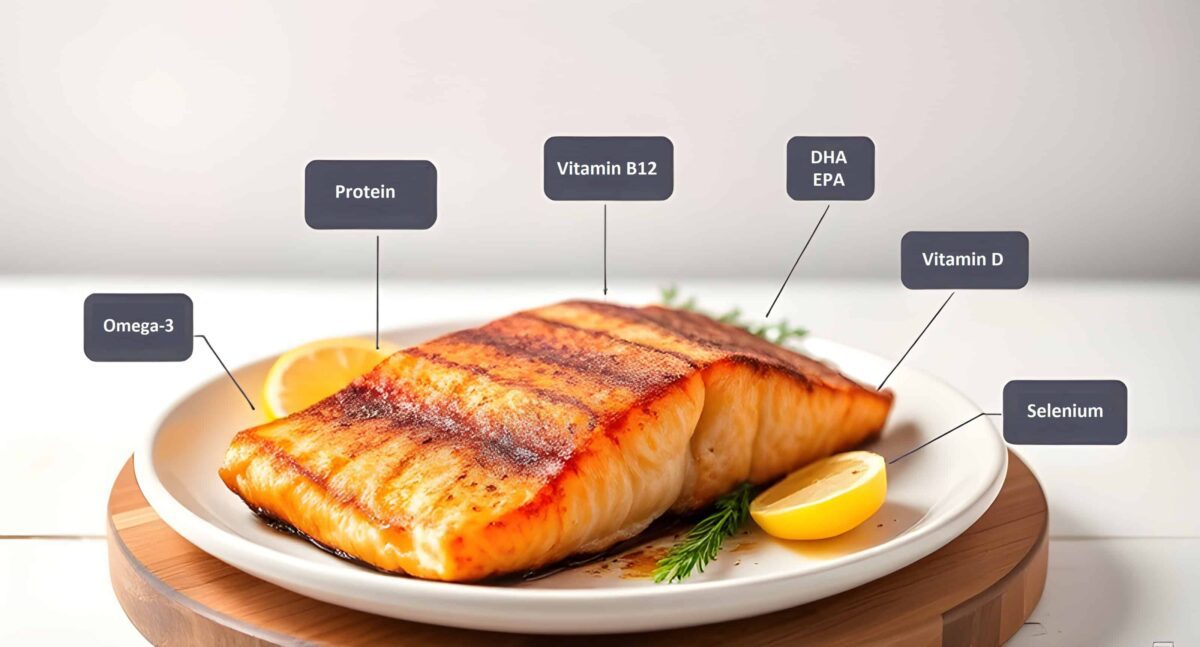
1. Salmon’s Nutritional Profile
Salmon Nutrition Facts highlight why this fish is a staple in many healthy diets. Renowned for its exceptional nutritional benefits, salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, which support heart and brain health. Exploring Salmon Nutrition Facts reveals that it is also packed with essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, selenium, and B vitamins.
In addition to being a high-protein, low-saturated-fat option, salmon is ideal for those aiming to lose weight or enhance their overall health. Here are some of the key nutrients found in salmon:
- Vitamin D: Supports bone health and strengthens the immune system.
- Selenium: Functions as an antioxidant, safeguarding cells against damage.
- B Vitamins: Vital for energy production and maintaining nerve function.
With such an outstanding nutritional profile, salmon is an excellent choice for a balanced diet, offering numerous health benefits to promote overall well-being.
2. The Powerful Health Benefits of Salmon
Salmon is packed with nutrients, offering many salmon health benefits when eaten right. It’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help lower inflammation, boost heart health, and support brain function. Many ask is salmon good for you, and the answer is a big yes. It’s full of nutrients and can help prevent chronic diseases.
Salmon can lower the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. But, it’s key to know the potential risks of eating salmon like mercury and PCBs. To avoid these, pick wild-caught or farmed salmon from trusted sources.
Here are some of the key benefits of salmon consumption:
- Reduces inflammation and improves heart health
- Supports brain function and may reduce the risk of depression
- May reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon and breast cancer
- Supports eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration
In conclusion, salmon is a nutritious food with many health benefits. By choosing wild-caught or sustainably farmed salmon and knowing the potential risks of eating salmon, you can enjoy its benefits. So, is salmon good for you? Absolutely, and it’s a great choice for a healthy diet.
| Salmon Type | Omega-3 Content | Mercury Content |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught salmon | High | Low |
| Farmed salmon | Medium | Medium |

3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Heart of Salmon’s Benefits
Salmon is known for its incredible health benefits, primarily due to its high omega-3 fatty acid content. These essential fatty acids, EPA and DHA, are powerful allies in reducing inflammation and improving heart health. They also support brain function and cognitive well-being. So, is salmon good for you? Absolutely, and a lot of it is thanks to its omega-3 content.
Omega-3 fatty acids in salmon provide numerous benefits, including lowering triglycerides, reducing blood pressure, and preventing blood clots, which together contribute to a healthier heart. They also play a significant role in brain health, potentially reducing depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. If you’re curious about why eating salmon feels so good, you can learn more in this detailed guide: Why Eating Salmon Feels Better.
EPA and DHA Explained
EPA and DHA are the primary omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon. These are vital for heart health, brain development, and overall wellness. Including salmon in your diet is a smart choice if you’re looking to increase your intake of these essential nutrients.
Recommended Daily Intake
Health experts recommend consuming 250-500 mg of EPA and DHA daily for adults. A 3-ounce serving of salmon delivers approximately 1.8-2.2 grams of omega-3 fatty acids, making it an excellent source.
Impact on Brain Health
Research highlights that omega-3 fatty acids in salmon are beneficial for brain health. They help brain cells function more effectively, improving focus, memory, and mood. Adding salmon to your meals is a proactive way to support your mental well-being.
In summary, omega-3 fatty acids are the cornerstone of salmon’s health benefits. They contribute to heart health, enhance brain function, and make salmon a highly nutritious food. With its impressive EPA and DHA content, salmon is a top pick for a healthy, balanced diet.
Let me know if you’d like further edits!
| Omega-3 Fatty Acid | Benefits | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|
| EPA | Heart Health, Inflammation Reduction | 250-500 mg |
| DHA | Brain Development, Cognitive Function | 250-500 mg |
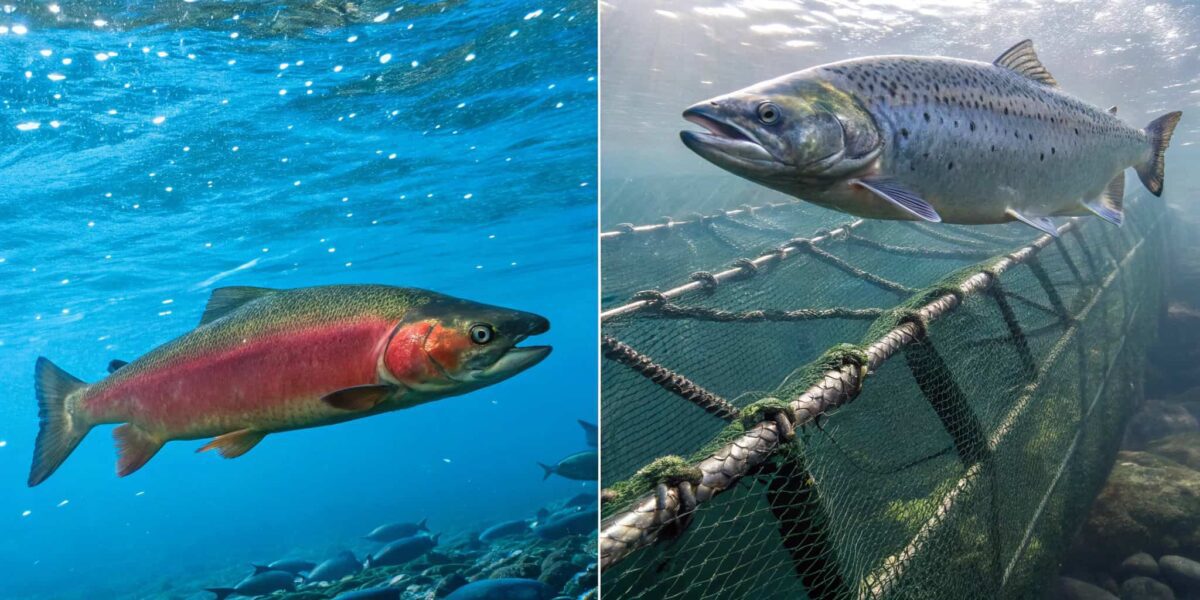

4. Wild vs. Farmed Salmon: What’s the Difference?
There are two main types of salmon: wild and farmed. The difference between wild salmon vs. farmed salmon is key to your health and the planet. Wild salmon has more omega-3s and less saturated fat, making it healthier.
Farmed salmon might have more mercury in salmon. Mercury is harmful, affecting pregnant women and kids. Wild salmon, on the other hand, has less mercury and PCBs, which are cancer-causing.
Here are some key differences between wild and farmed salmon:
- Wild salmon: Higher in omega-3 fatty acids, lower in saturated fat, and lower levels of mercury and PCBs
- Farmed salmon: Higher in saturated fat, higher levels of mercury and PCBs, and potential for antibiotic use
So, is farm-raised salmon unhealthy? It’s not unhealthy, but it has risks. Wild salmon is safer for your health and the environment. Yet, some farms are improving their practices.
In conclusion, choosing between wild and farmed salmon depends on your values. Knowing the differences helps you make a choice that’s good for you and the planet.
| Type of Salmon | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Saturated Fat | Mercury Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild Salmon | Higher | Lower | Lower |
| Farmed Salmon | Lower | Higher | Higher |
5. Is There Anything Unhealthy About Salmon?
Salmon is a nutritious food, but it has some health risks. The main concern is mercury in salmon. Mercury levels in salmon can change based on the type and where it was caught.
There’s also a risk of PCBs, or polychlorinated biphenyls, in some salmon. Health risks of eating salmon can grow if it’s farmed. This is because some farms use antibiotics to help the fish grow and stay healthy.
When thinking about salmon’s health risks, consider these points:
- Mercury levels in the salmon
- PCB exposure risks
- Antibiotic use in farmed salmon
Even with risks, choosing wild-caught salmon can help. Being aware of is there anything unhealthy about salmon? lets you enjoy its benefits while reducing risks.
| Type of Salmon | Mercury Levels | PCB Exposure Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught salmon | Lower | Lower |
| Farmed salmon | Higher | Higher |
6. Best Practices for Selecting Quality Salmon

Choosing quality salmon involves several key factors. You want it to be fresh and safe, and also sustainably sourced. This ensures the health of our oceans and the environment.
Look for freshness in salmon: a nice smell, firm texture, and shiny look. Check for MSC or ASC labels for responsible fishing or farming. For the best way to cook salmon, try grilling, baking, or poaching to keep its nutrients.
Signs of Fresh Salmon
- Fresh smell
- Firm texture
- Shiny appearance
Sustainable Sourcing Guidelines
When buying salmon, look for sustainable labels. Ask your fishmonger about the salmon’s origin and how it was caught or farmed. Choosing sustainable salmon sourcing and following salmon consumption safety guidelines helps our oceans.
Follow these tips for delicious, safe, and sustainable salmon. Always prioritize salmon consumption safety and choose the best way to cook salmon to keep its nutrients.
| Salmon Type | Sustainable Sourcing Certification | Origin |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught | MSC | Alaska |
| Farmed | ASC | Norway |
7. Optimal Cooking Methods for Maximum Health Benefits
Cooking salmon right is key to keeping its omega-3 fatty acids and nutrients intact. Grilling, baking, and poaching are top choices because they use less heat and time. These methods help keep salmon’s health benefits in check.
When cooking salmon, consider these important points:
- Grilling: It gives a crispy outside and a soft inside. It’s great for keeping salmon’s natural taste and health benefits.
- Baking: This method is low in fat and keeps salmon moist. It’s also easy to add flavors with herbs and spices.
- Poaching: It’s a moist heat method that’s perfect for salmon. It keeps the fish’s texture and taste, making it a top choice for health benefits.
Choosing the right cooking method lets you enjoy salmon’s health perks and taste. Whether you grill, bake, or poach, aim for gentle and quick cooking. This way, you get the most out of your salmon and its amazing health benefits.
The best cooking methods for salmon focus on keeping nutrients and flavor. By doing this, you unlock salmon’s full health benefits and enjoy a tasty, healthy meal.
| Cooking Method | Temperature | Cooking Time |
|---|---|---|
| Grilling | 400°F (200°C) | 4-6 minutes per side |
| Baking | 375°F (190°C) | 8-12 minutes |
| Poaching | 180°F (82°C) | 8-12 minutes |
8. Environmental Impact and Sustainable Consumption
When we talk about eating salmon, we must think about how it affects the planet. The high demand for salmon has caused worries about overfishing. This can harm wild salmon populations and upset the balance of marine life.
Aquaculture, or farm-raised salmon, also raises sustainable salmon sourcing concerns. It can lead to water pollution and the spread of diseases.
The debate about salmon health concerns centers on whether is farm-raised salmon unhealthy. While it’s cheaper and easier to find, we must consider its health risks. Choosing sustainable salmon sourcing helps lessen the environmental damage and supports better fishing methods.
- Look for certifications like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC), which ensure that salmon is sourced sustainably.
- Choose wild-caught salmon when possible, as it tends to have lower levels of contaminants and higher nutritional value.
- Support local fisheries and fishing communities to promote more sustainable and responsible fishing practices.
By being careful about our salmon choices and picking sustainable salmon sourcing, we can make a difference. This helps reduce harm to the environment and supports a healthier food system.

9. Safe Consumption Guidelines and Recommendations
When it comes to salmon consumption safety, there are several factors to consider. Salmon is nutritious, but there are risks. To stay safe, it’s important to follow guidelines.
One big concern is mercury contamination. Choosing wild-caught salmon over farmed can help. Also, is salmon bad for you if you’re pregnant or have health issues? No, but it’s key to stick to recommended amounts and how often to eat it.
Here are some guidelines for safe salmon consumption:
- Choose wild-caught salmon whenever possible
- Limit serving sizes to 8-12 ounces per week
- Avoid eating salmon if you have a weakened immune system
- Cook salmon to an internal temperature of at least 145°F
By following these guidelines, you can enjoy salmon’s health benefits while avoiding risks. Always prioritize salmon consumption safety for a healthy meal.
For more info on safe eating, talk to a healthcare pro or a dietitian. They can give you personalized advice on adding salmon to your diet safely.
| Salmon Type | Mercury Level | Recommended Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught | Low | 8-12 ounces per week |
| Farmed | Higher | 4-6 ounces per week |
10. Special Considerations for Pregnant Women and Children
Pregnant women and children have special nutritional needs. The FDA has guidelines for eating salmon during these times. These guidelines help balance the benefits of salmon with the need to avoid harmful contaminants like mercury.
When thinking about is salmon good for you, it’s important to consider the risks. For pregnant women and kids, the FDA suggests eating salmon in small amounts. This helps keep exposure to harmful substances low while still getting the good stuff from salmon.
Some key things to keep in mind include:
- Choose low-mercury salmon like wild-caught Alaskan or Pacific salmon.
- Stick to 6 ounces or less of salmon per week.
- Stay away from high-mercury fish like shark, swordfish, and king mackerel.
By following these tips, pregnant women and children can enjoy salmon’s benefits. They can do this while keeping their exposure to harmful substances low.
| Salmon Type | Mercury Level | Recommended Portion Size |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught Alaskan salmon | Low | 6 ounces or less per week |
| Farmed salmon | Moderate | 3 ounces or less per week |
| High-mercury fish (shark, swordfish, king mackerel) | High | Avoid |
11. The Recipe
Print
Baked Garlic Butter Salmon with Asparagus
- Total Time: 25 minutes
- Yield: 4 servings
Description
This Baked Garlic Butter Salmon with Asparagus is a stunning yet simple dish that combines the richness of salmon with the freshness of roasted asparagus. The garlic butter glaze adds a layer of indulgence while keeping the meal light and healthy.
Perfect for busy weeknights or a casual dinner party, this dish is as versatile as it is delicious. The tender salmon paired with crisp asparagus creates a beautiful balance of textures and flavors, all tied together by the zesty lemon. Serve it with a side of rice, potatoes, or enjoy it on its own for a low-carb delight!
Ingredients
– 4 salmon fillets (6 oz each)
– 1 lb asparagus, trimmed
– 3 tablespoons unsalted butter, melted
– 2 tablespoons olive oil
– 4 garlic cloves, minced
– 1 lemon (zested and juiced)
– 1 teaspoon paprika
– Salt and freshly ground black pepper to taste
– 1 teaspoon fresh parsley, chopped (for garnish)
Instructions
1. Preheat the oven to 400°F (200°C) and line a baking sheet with parchment paper.
2. Arrange the salmon fillets on one side of the baking sheet and the asparagus on the other side.
3. In a small bowl, whisk together melted butter, olive oil, minced garlic, lemon juice, and zest. Add paprika, salt, and pepper to taste.
4. Brush the butter mixture generously over the salmon fillets and drizzle some over the asparagus. Toss the asparagus gently to coat.
5. Bake in the preheated oven for 12-15 minutes, or until the salmon is flaky and the asparagus is tender-crisp.
6. Garnish with fresh parsley and serve immediately with lemon wedges.
- Prep Time: 10 minutes
- Cook Time: 15 minutes
FAQ
What are the health benefits of salmon?
Salmon is packed with omega-3s, which are good for your heart and brain. It also has lots of protein, vitamins, and minerals. This makes it a superfood for your health.
What are the nutrition facts for salmon?
Salmon is full of vitamins like D and B vitamins. It’s also high in protein and low in fat. This makes it great for your health and weight management.
What is the difference between wild salmon and farmed salmon?
Wild salmon has more omega-3s and less fat than farmed salmon. Farmed salmon might have more mercury and PCBs. The nutritional differences are important to consider when choosing salmon.
What are the potential health risks of eating salmon?
Salmon is mostly healthy, but there are risks. These include mercury, PCBs, and antibiotics in farmed salmon. Choosing wild-caught and eating it in moderation can help.
Is salmon good for you?
Yes, salmon is very healthy. It’s full of omega-3s, protein, and vitamins. It’s good for your heart and brain. But, be aware of mercury and PCBs and eat it in balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, salmon is a nutritious food that offers numerous health benefits. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids and high-quality protein, it is a valuable addition to any diet. However, it’s equally important to be aware of potential risks, such as mercury levels and the methods used for catching or farming the fish.
Understanding Salmon Nutrition Facts and the differences between wild-caught and farmed salmon can help you make informed decisions. Opting for sustainably sourced salmon is essential for both your health and the environment. By familiarizing yourself with Salmon Nutrition Facts and following safe cooking and consumption guidelines, you can maximize its benefits. Incorporating salmon into your diet is an excellent way to boost overall well-being.

